Forging is a critical manufacturing process used in the production of a wide range of components for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, and more. Within the forging process, there are different methods, including open-die and closed-die press forging, each with its unique characteristics and applications. In this blog, we will explore the differences between open-die and closed-die press forging units, with a focus on the forging industry in Ludhiana and Punjab, known for its expertise in forging.
Forging Units in Ludhiana and Punjab
Ludhiana and Punjab are renowned for their forging industry, with numerous forging units that specialize in producing high-quality forged components for various applications, including automotive, agriculture, and more. These forging units are equipped with state-of-the-art machinery, skilled labour, and extensive experience in the forging process, making them a hub for forging in India.
Difference between Open-Die and Closed-Die Press Forging
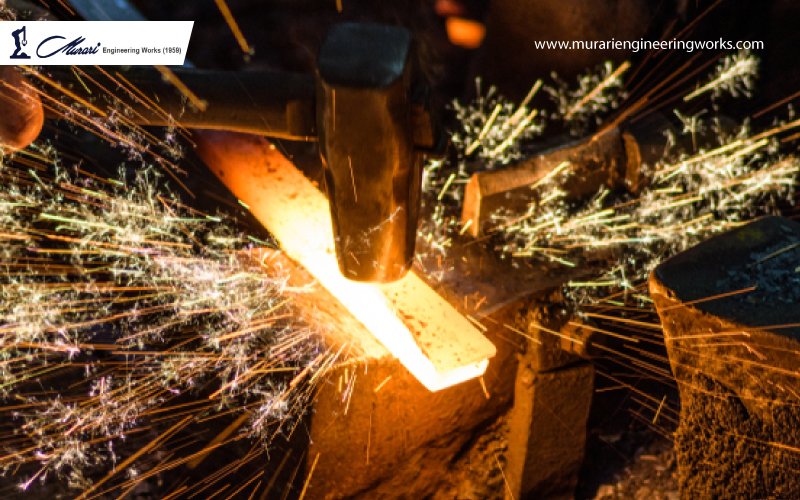
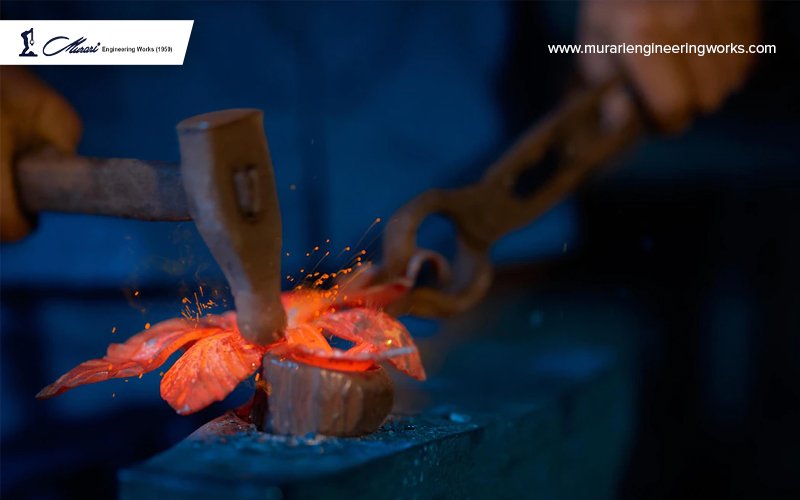
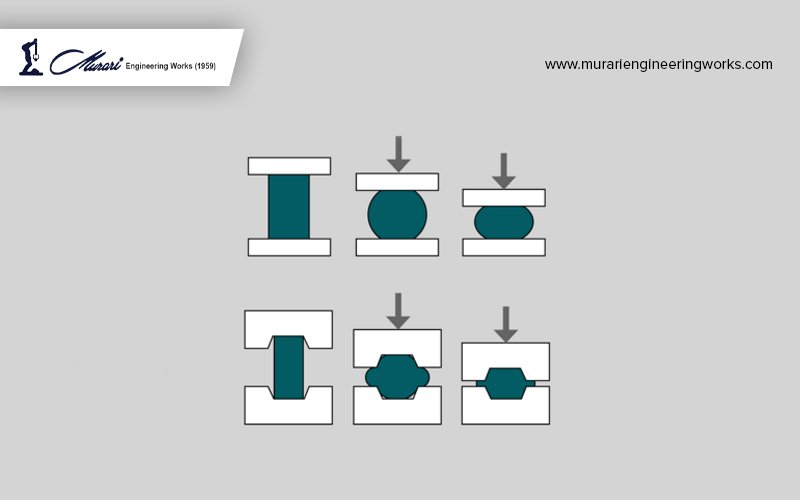
Open-Die Forging: Open-die forging, also known as free forging or smith forging, is a process where a workpiece is shaped between two flat or slightly contoured dies without completely enclosing the material. The dies are not fully closed, allowing the material to flow and take the shape of the dies. Open-die forging is commonly used for producing large, heavy, and complex-shaped components, such as shafts, discs, and blocks.
The open-die forging process involves heating the material to its plastic deformation temperature, placing it on the anvil or hammer, and then striking it with a hammer or press to shape it. The material is deformed and shaped by repeated blows until the desired shape is achieved. This process requires skilled labour to control the shape, size, and dimensions of the component accurately. Open-die forging results in components with a rough surface finish and requires additional machining and finishing operations to achieve the final desired specifications.
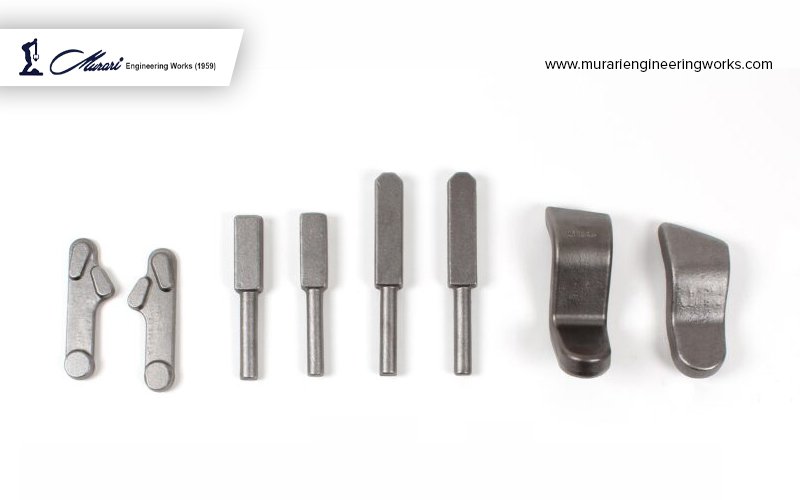
Closed-Die Press Forging: Closed-die press forging, also known as impression die forging, is a process where the workpiece is completely enclosed within the dies, which are pre-designed to form the desired shape of the component. The material is heated to its plastic deformation temperature and then placed between the dies, which are then closed using a press to shape the material. The closed-die forging process results in components with precise shapes, sizes, and dimensions, requiring minimal or no further machining operations.
Closed-die press forging is commonly used for producing small to medium-sized components with complex shapes and tight tolerances, such as gears, connectors, and bolts. It offers excellent dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material utilization, making it a preferred choice for producing high-quality components with consistent properties.
Key Differences Between Open-Die and Closed-Die Press Forging
- Material Flow: In open-die forging, the material flows and deforms freely between the dies, resulting in a less precise shape and surface finish. On the other hand, in closed-die press forging, the material is completely enclosed within the dies, resulting in a more precise shape and surface finish.
- Complexity of Shapes: Open-die forging is suitable for producing large and complex-shaped components, while closed-die press forging is ideal for producing smaller to medium-sized components with intricate shapes and tight tolerances.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Closed-die press forging offers higher dimensional accuracy compared to open-die forging due to the controlled environment within the dies, resulting in components with precise shapes, sizes, and dimensions.
- Surface Finish: Open-die forging results in components with a rough surface finish, requiring additional machining and finishing operations, while closed-die press forging produces components with a smoother surface finish, reducing the need for additional finishing operations.
- Material Utilization: Closed-die press forging offers higher material utilization compared to open-die forging. In open-die forging, due to the free flow of material between the dies, there may be more material wastage, resulting in lower material utilization. On the other hand, in closed-die press forging, the material is enclosed within the dies, allowing for better material utilization and reduced material wastage.
- Production Rate: Open-die forging may have a slower production rate compared to closed-die press forging due to the repeated blows required to shape the material and the need for additional machining and finishing operations. In contrast, closed-die press forging can have a higher production rate as it produces components with precise shapes and dimensions, reducing the need for additional machining operations.
- Cost: The cost of open-die forging may be lower in terms of initial tooling and die costs, as the dies are not fully enclosed and may be simpler in design. However, the overall cost may increase due to the need for additional machining and finishing operations. On the other hand, closed-die press forging may have higher initial tooling and die costs, as the dies are fully enclosed and require precise design and manufacturing. However, the overall cost may be lower due to higher material utilization and reduced need for additional finishing operations.
Importance of Open-Die and Closed-Die Press Forging
Both open-die and closed-die press forging have their unique importance in the manufacturing industry, and their choice depends on the specific requirements of the components being produced. Open-die forging is suitable for producing large and heavy components with complex shapes, where material flow and deformation are critical. It allows for flexibility in shaping and forming components that may not be possible with other methods. Open-die forging is commonly used in the production of components for industries such as aerospace, energy, and heavy equipment.
On the other hand, closed-die press forging is ideal for producing smaller to medium-sized components with precise shapes, sizes, and dimensions. It offers higher dimensional accuracy, better surface finish, and improved material utilization, making it a preferred choice for producing high-quality components with consistent properties. Closed-die press forging is commonly used in the production of components for industries such as automotive, agriculture, and machinery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, open-die and closed-die press forging are two different methods of forging with their unique characteristics and applications. Open-die forging is suitable for producing large and heavy components with complex shapes, while closed-die press forging is ideal for producing smaller to medium-sized components with precise shapes and dimensions. Both methods have their importance in the manufacturing industry, and their choice depends on the specific requirements of the components being produced. The forging industry in Ludhiana and Punjab is well-known for its expertise in both open-die and closed-die press forging, providing high-quality forged components for various industries. Whether it’s the flexibility of open-die forging or the precision of closed-die press forging, both methods play a crucial role in the production of automotive parts, agricultural equipment, and other critical components used in various industries.